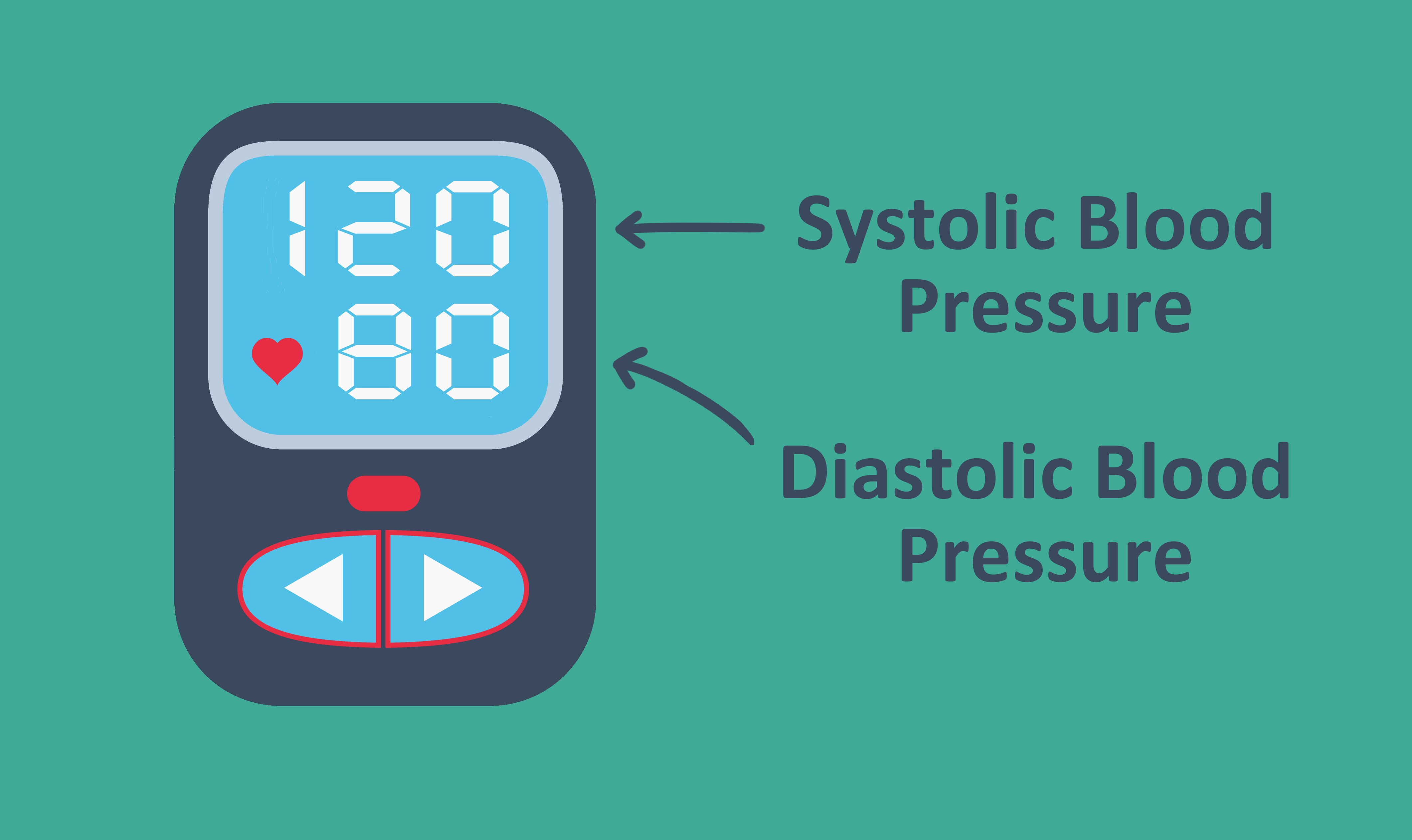
Blood pressure (BP) is the force of blood on the artery walls as blood is pumped through the body.1,2 Systolic blood pressure is the maximum pressure within the artery during the ejection period of ventricular systole.1-3 Diastolic blood pressure is the lowest pressure in the vessel immediately before the next systole.
The 2017 hypertension guidelines from the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) detail the proper methods for the accurate measurement and documentation of blood pressure.4 It defines both systolic and diastolic pressures. Hypertension is persistent blood pressure is ≥ 130 mm Hg systolic OR ≥ 80 mm Hg diastolic. Persistence is determined if the average of two or more careful blood pressure readings on two or more occasions are above the threshold.
Systolic blood pressure measures the pressure while the heart is beating while diastolic measures the pressure while the heart is at rest. Systolic comes from the Latin systolicus and Greek systole, meaning a drawing together or contraction. In modern medicine, systole has come to mean the contraction of the heart and arteries. Diastolic comes from the Latin and Greek diastole, meaning drawing asunder or dilation. In modern medicine, diastole has come to mean the relaxation of the heart and arteries that occurs as part of the normal rhythmic process of a heartbeat.
References
- Ogedegbe G, Pickering T. Principles and techniques of blood pressure measurement. Cardiol Clin 2010; 28 (4): 571-586.
- Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, et al. Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: Part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension 2005; 45 (1): 142-161.
- Thulin T, Andersson G, Schersten B. Measurement of blood pressure--a routine test in need of standardization. Postgrad Med J 1975; 51 (596): 390-395.
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2017.
.png)

